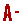
The brain is a highly complex organ that plays an essential role not just in thinking but in all body functions. It’s divided into two halves, the right and left brain. Specific areas are responsible for different functions, but the brain works as a whole.
How the human brain works.
The human brain is an intricate organ. At approximately 3 pounds, it contains about 100 billion neurons and 100 trillion connections. Your brain is the command center for all that you think, feel, and do.
Your brain divides into two halves or hemispheres. Within each half, particular regions manage certain functions. The two sides of your brain look very much alike, but there’s a huge difference in how they process information. Despite their contrasting styles, the two halves of your brain don’t work independently of each other.
Nerve fibers connect different parts of your brain. If a brain injury severs the connection between sides, you might still function typically. But the lack of integration would cause some impairment. The human brain constantly reorganizes itself. It’s adaptable to change, whether it’s physical or through life experience. It’s tailor-made for learning.
As scientists continue mapping the brain, we gain more insight into which parts control necessary functions. This information is vital to advancing research into brain diseases and injuries, and how to recover from them.
The left brain vs. right brain myth
The theory is that people are either left-brained or right-brained, meaning that one side of their brain is dominant. If you’re mostly analytical and methodical in your thinking, the theory says that you’re left-brained. If you tend to be more creative or artistic, you’re right-brained.
This theory is based on the fact that the brain’s two hemispheres function differently. This first came to light in the 1960s, thanks to the research of psychobiologist and Nobel Prize winner Roger W. Sperry. The left brain is more verbal, analytical, and orderly than the right brain. It’s sometimes called the digital brain. It’s better at things like reading, writing, and computations.
We know the two sides of our brain are different, but does this necessarily mean that we have a dominant brain just as we have a dominant hand? A team of neuroscientists set out to test this premise. In a 2013 research reviewTrusted Source, they found no proof that this theory is correct. Magnetic resonance imaging of 1,000 people revealed that the human brain doesn’t actually favor one side over the other. The networks on one side aren’t generally stronger than the networks on the other side.
Bundles of nerve fibers tie the two hemispheres together, creating an information highway. Although the two sides function differently, they work together and complement each other. You don’t use only one side of your brain at a time. Whether you perform a logical or creative function, you receive input from both sides of your brain. For example, people credit the left brain with language, but the right brain helps you understand context and tone. The left brain handles mathematical equations, but the right brain helps out with comparisons and rough estimates.
General personality traits, individual preferences, or learning styles don’t translate into the notion that you’re left-brained or right-brained. Still, it’s a fact that the two sides of your brain are different, and certain areas of your brain do have specialties. The exact areas of some functions can vary a bit from person to person.
Tips for keeping your brain sharp
According to the Alzheimer’s Association, keeping your brain active via mentally challenging activities, like learning a new skill, may have benefits for brain health in the short and long term. They also suggest that a lack of mental stimulation may increase the chance of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
Here are a few tips to stimulate your brain:
Tips and tricks
- Spend some time each day reading, writing, or both.
- Never stop learning. Take a class, go to a lecture, or try to acquire a new skill.
- Complete challenging crossword and Sudoku puzzles.
- Play memory games, board games, card games, or video games.
- Take on a new hobby that requires you to focus, like learning a new language or a musical instrument.
Tips for boosting creativity
If you would like to nourish your creative side, here are a few ways to get started:
- Read about and listen to the creative ideas of others. You might discover the seed of an idea you can grow or set your own imagination free.
- Try something new. Take up a creative hobby, such as playing an instrument, drawing, or storytelling. A relaxing hobby can help your mind wander to new places.
- Look within. This can help you gain a deeper understanding of yourself and what makes you tick. Why do you gravitate toward certain activities and not others?
- Keep it fresh. Break your set patterns and go outside your comfort zone. Take a trip to a brand-new place. Immerse yourself in another culture. Take a course in an unfamiliar subject.
Tips and tricks
- When you get new ideas, write them down and work on developing them further.
- Brainstorm. When you face a problem, try to find several ways to get to a solution.
- When doing simple chores, such as washing the dishes, leave the TV off and let your mind wander to new places.
- Rest, relax, and laugh to let your creative juices flow.
Resources: Healthline: How The Human Brain Works
URL: https://www.healthline.com/health/left-brain-vs-right-brain#How-the-human-brain-works
Date of Input: 26/01/2023 | Updated: 22/10/2024 | aslamiah
MEDIA SHARING